Description
(30 points)
HARD HARD HARD HARD HARD
The skyline of a city is the outer contour (外輪廓) formed by all the buildings when viewed from a distance. You are given several rectangular buildings, and your task is to compute the key points that form the skyline.
Each building is represented as a triplet [Li, Ri, Hi] where:
-
Liis the x-coordinate of the left edge, -
Riis the x-coordinate of the right edge, -
Hi is the height of the building.
All buildings sit on a flat ground at height 0.
You must return the skyline formed by these buildings as a list of key points. A key point [x,y] represents a position where the skyline height changes from the previous height.
The key points must be sorted by increasing x-coordinate, and redundant horizontal points (same height continuing) must not be included.The final skyline should reflect the exact outer contour as viewed from left to right.
HINT
Here is part of the solution. Please complete the TODO sections.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// Structure to represent an edge (start or end of a building)
typedef struct {
int x;
int height;
int type; // 1 for start edge, 0 for end edge
} Edge;
// Comparison function for qsort to sort edges
int compareEdges(const void* a, const void* b) {
Edge* edgeA = (Edge*)a;
Edge* edgeB = (Edge*)b;
if (edgeA->x != edgeB->x) {
return edgeA->x - edgeB->x;
}
// If x-coordinates are the same, handle edge types:
// Start edges (type 1) with higher height come first
// End edges (type 0) with lower height come first
if (edgeA->type == 1 && edgeB->type == 1) {
return edgeB->height - edgeA->height;
}
if (edgeA->type == 0 && edgeB->type == 0) {
return edgeA->height - edgeB->height;
}
return edgeB->type - edgeA->type; // Start edges before end edges
}
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both the returned array and *returnColumnSizes array must be malloced,
* assume caller calls free().
*/
int** getSkyline(int** buildings, int buildingsSize, int* buildingsColSize,
int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
if (buildingsSize == 0) {
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
// Step 1: create start / end edges for all buildings
Edge* edges = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge) * buildingsSize * 2);
int edgeCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < buildingsSize; ++i) {
edges[edgeCount++] = (Edge){buildings[i][0], buildings[i][2], 1}; // start edge
edges[edgeCount++] = (Edge){buildings[i][1], buildings[i][2], 0}; // end edge
}
// Step 2: sort edges by x coordinate and edge type
qsort(edges, edgeCount, sizeof(Edge), compareEdges);
// Allocate result arrays (maximum possible size = number of edges)
int** result = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * edgeCount);
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * edgeCount);
*returnSize = 0;
/* ========================= TODOs start here ========================= */
// TODO 1:
// Sweep from left to right through the sorted edges.
// TODO 2:
// Maintain a data structure that keeps track of the heights of
// all "active" buildings (buildings that have started but not ended yet).
// TODO 3:
// When encountering a start edge, add its height to the active set.
// When encountering an end edge, remove its height from the active set.
// TODO 4:
// Important: if multiple edges share the same x coordinate,
// process ALL of them before deciding whether to output a skyline point.
// TODO 5:
// After processing all edges at position x,
// find the current maximum height among active buildings.
// TODO 6:
// If the current maximum height is different from the previous one,
// output a key point (x, current maximum height) and update the previous height.
/* ========================== TODOs end here ========================== */
free(edges);
return result;
}
int main(void)
{
int n;
// Input format:
// n
// L0 R0 H0
// L1 R1 H1
// ...
// Ln-1 Rn-1 Hn-1
if (scanf("%d", &n) != 1) {
return 0;
}
int **buildings = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int*) * n);
int *buildingsColSize = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
buildings[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 3);
int L, R, H;
if (scanf("%d %d %d", &L, &R, &H) != 3) {
for (int k = 0; k <= i; ++k) {
free(buildings[k]);
}
free(buildings);
free(buildingsColSize);
return 0;
}
buildings[i][0] = L;
buildings[i][1] = R;
buildings[i][2] = H;
buildingsColSize[i] = 3;
}
int returnSize;
int *returnColumnSizes;
int **skyline = getSkyline(buildings, n, buildingsColSize,
&returnSize, &returnColumnSizes);
// Print result
// Each line: x y
for (int i = 0; i < returnSize; ++i) {
printf("%d %d\n", skyline[i][0], skyline[i][1]);
}
// Free memory
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
free(buildings[i]);
}
free(buildings);
free(buildingsColSize);
if (skyline != NULL) {
for (int i = 0; i < returnSize; ++i) {
free(skyline[i]);
}
free(skyline);
}
if (returnColumnSizes != NULL) {
free(returnColumnSizes);
}
return 0;
}
Input
-
The input is a 2D integer array
buildings. -
The first line is the number of buildings
-
Each element
buildings[i] = [Li, Ri, Hi]describes:-
Li: the x-coordinate of the building’s left boundary
-
Ri: the x-coordinate of the building’s right boundary
-
Hi: the height of the building
-
-
Constraints:
-
0 ≤ Li< Ri
-
Hi > 0
-
-
Buildings may overlap.
Take Sample Input 1 as example,
Each line contains three integers described as above. We can visulized in the Figure 1.
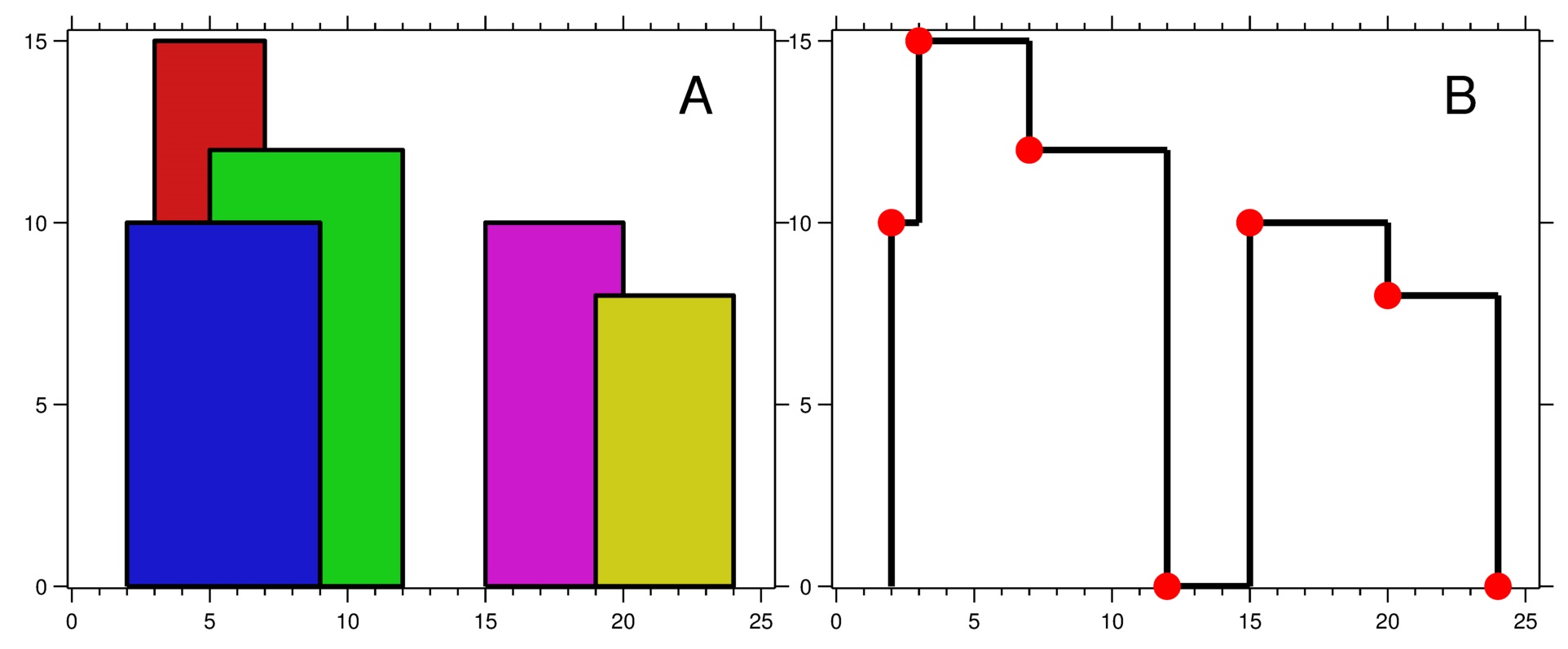
Figure 1
Output
-
Output a 2D integer array
skyline. -
Each element
skyline[j] = [xj, yj]is a key point, indicating the skyline height becomesyjat x-coordinatexj. -
Requirements:
-
Key points must be sorted by increasing
xj. -
Do not include multiple points with the same height in a row. Only include points where the height actually changes.
-
The skyline typically ends with a point whose height becomes 0.
-
The Sample Output 1 can be inllustrated as Figure 1.
Note that There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline.
The following instance is not acceptable;
2 3 4 5 7 5 11 5 12 7
the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such
2 3 4 5 12 7