Description
You are given two rooted binary trees, $X$ and $Y$, in a special format, each with $N$ vertices, numbered from $0$ to $N-1$. The format is described by the following EBNF (Extended Backus–Naur form):
The tree $X$: TREE ::= '(' INT '/' TREE '/' TREE ')' | NIL
The tree $Y$: TREE ::= INT '(' TREE ')' '(' TREE ')' | NIL
It means that a tree is a integer followed by two subtrees or a NIL. The integer represents which vertex the root of the tree is. If the tree is a NIL, it means that the tree is empty.
Two binary trees are considered identical if and only if:
- Both trees are empty (NIL), or
- Both trees have roots, and:
- Their root values are equal AND
- Their left subtrees are identical AND
- Their right subtrees are identical
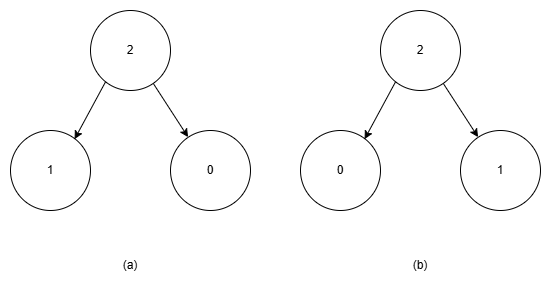
Here is a example. In the following figure, tree (a) will be represented as (2/(1//)/(0//)) and 2(1()())(0()()),
tree (b) as (2/(0//)/(1//)) and 2(0()())(1()()), and they are NOT identical.
Input
Input contains three lines. The first line contains an integer $N$, the number of vertices in each tree.
For the following two lines, each line contains a string, representing tree $X$ and $Y$ respectively in the EBNF format.
Contraints
- $1 \leq N \leq 10^5$
- Length of $X$ and $Y$ won't exceed $10^6$
- $X$ only contain character
'(',')','/'and digit. - $Y$ only contain character
'(',')'and digit.
Output
If the two trees are identical, output "YES", otherwise output "NO" (without quote)
Noted that you should output one single line.