Description
Yoshirin and Micchi will spend their Golden Week vacation in Taiwan. However, their vacation plan has not been completed, because they couldn't stay serious when discussing it. Now they need a trip recommendation system to plan their itineraries. Yoshirin and Micchi have made a wish list about tourist attractions they want to visit. Each tourist attraction is scored by their preference from 1 to 5. To save time, they hope to spend less time traveling among tourist attractions. Also, they prefer popular trip itineraries, so they will visit the tourist attractions base on the constant tourist flow. Please build a trip recommendation system to help Yoshirin and Micchi.
In the system, a map will be represented as a graph, in which the nodes stand for the places listed by the user, and the edges stand for the accesses between every two places. In other words, every node is adjacent to each other. Between every two nodes exists two edges with opposite directions. There are two kinds of graphs. The first graph is about the travel time. In this graph, the edge weights are the time consumption of people traveling from one place to another. The second graph is about the tourist flow. In real life, tourist flow records the amount of people traveling from one place to another. Here we take tourist flow as the tendency of people traveling to different places. In this graph, the edge weights are the tendency values, where higher values stand for the higher tendency that people to travel from one place to another.
The system is supposed to guide users to any places with the optimal path in terms of either travel time or tourist flow. Unfortunately, some places are closed due to the pandemic situation recently. The places that have been closed should not be recommended to the users.
The system should help users find an optimal path given the origin and destination. When concerning the travel time, the path that costs the least time will be optimal. When concerning the tourist flow, the path that is the most possible to be taken will be optimal. You can regard tourist flow as a kind of probability. Please see the hint. If there are multiple optimal paths, first, choose the path with the highest sum of preference scores as the result. If there are still multiple optimal paths with the same total preference scores, choose the path that first leads to the place with the smallest index. Please see the figure below.
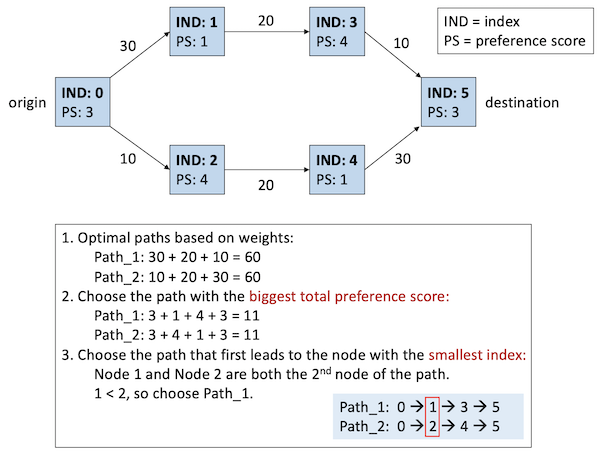
The system will accept 5 kinds of instructions, described as follows.
1. SET_ORIGIN
Assign a place as the origin of the traveling itinerary. The origin will not change until we reset it.
- Usage: SET_ORIGIN %PLACE_NAME
- Parameters:
- %PLACE_NAME: place name, a string containing no spaces
- Example:
- SET_ORIGIN Taipei_101 : Set Taipei_101 as the origin of the trip.
2. MARK_STATE
Mark the state for a set of places with “open” or “close”. If a place is open, that place can be visited; otherwise, that place cannot be visited. All the places are open in the beginning. The states of the places will not change even though the origin is reset (SET_ORIGIN %PLACE_NAME).
- Usage: MARK_STATE %TO_STATE %PLACE_NAME_0 %PLACE_NAME_1 …
-
Parameters:
- %TO_STATE: state of the place(s) in future
- OPEN: Reopen the places, which will become visitable.
- CLOSE: Close the places, which will become not visitable.
- %PLACE_i: place name(s). a string without spaces
- [Note] 0≦i≦N-1, N is the total number of places.
- [Note] Place names are separated by one space.
- %TO_STATE: state of the place(s) in future
-
Example:
- MARK_STATE CLOSE Palace_Museum Taipei_101 : Mark Palace_Museum and Taipei_101 as close.
- MARK_STATE OPEN Taipei_101 : Mark Taipei_101 as open.
3. OPTIMAL_PATH
Choose a place as the destination of the trip. In terms of the assigned consideration, find the optimal path.
- Usage: OPTIMAL_PATH %DEST %CONSIDERATION
- Parameters:
- %DEST: place name, a string without spaces
- %CONSIDERATION: the consideration for finding the optimal path
- TIME: travel time
- FLOW: tourist flow
- Example:
- OPTIMAL_PATH Shilin_Night_Market TIME : Find the optimal path from the current origin to Shilin_Night_Market in terms of travel time.
4. LIMITED_PATH
Choose a place as the destination of the trip. Decide a number K (2≦K≦100), which is the maximum number of stops the user wants to visit. The origin is the first stop and the destination is the last stop. Find the locally optimal path in terms of the assigned consideration. If the destination cannot be accessed within K places, there is no such path.
- Usage: LIMITED_PATH %DEST %CONSIDERATION %MAX
- Parameters:
- %DEST: place name, a string without spaces
- %CONSIDERATION: Travel time or tourist flow
- TIME: travel time
- FLOW: tourist flow
- %MAX: the maximum number of stops the user wants to visit (the K above)
- Example:
- LIMITED_PATH Shilin_Night_Market FLOW 3 : Within 3 stops, find the optimal path from the current origin to Shilin_Night_Market in terms of travel time. Note that the origin and the destination are also counted in the stops.
5. END_OF_INSTRUCTION
Stop receiving instructions.
Input
The following elements will appear in order.
- The number of places (N) on the system's map.
- 2 ≦ N ≦ 100
-
N lines of place information
-
%PLACE_INDEX %PLACE_NAME %PLACE_PS
-
%PLACE_INDEX: index of the place, from 0 to N-1 in order
-
%PLACE_NAME: places' name represented with a string
-
%PLACE_PS: users' preference score for the place
-
-
-
An N*N matrix contains integer values
- Non-zero values represent the edges' weights (time consumption in minutes) between nodes.
- Zeros exist only on the diagonal, representing no self-loop edges.
- Each value is between 0 and 231-1
- An empty line
-
An N*N matrix contains double values
- Non-zero values represent the edges' weights (tourist tendency) between nodes.
- Zeros exist only on the diagonal, representing no self-loop edges.
- Each value is between 0.1 and 0.9 (0.1 ≦ values ≦ 0.9)
-
Several instructions
- E.g. SET_ORIGIN, MARK_STATE, OPTIMAL_PATH, FEASIBLE_PATH, END_OF_INSTRUCTION
- SET_ORIGIN must be the first instruction, but it might appear several times later to change the origin.
- END_OF_INSTRUCTION is the last instruction, and it will appear only once.
Output
The output of SET_ORIGIN:
- If %PLACE_NAME can be set as the origin, print "%PLACE_NAME is the new origin"
- If %PLACE_NAME cannot be set as the origin, print "Fail to reset the origin"
- Possible cause: The state of the place is close.
The output of MARK_STATE:
According to the order in the instruction, for each place that we try to mark:
- If the place can be successfully marked, print nothing.
- If the place cannot be marked, print "Fail to open %PLACE_i" or "Fail to close %PLACE_i" line by line.
- 0 ≦ i ≦ M-1, where M is the number of places in the instruction.
- There will be at most M lines to print.
- Possible cause 1: Trying to mark the place with its original state.
- Possible cause 2: Trying to mark the origin with CLOSE.
The output of OPTIMAL_PATH:
- If the path can be found, print the optimal path from the current origin to the destination, in the format "Optimal %CONSIDERATION : %PLACE_NAME -> %PLACE_NAME -> ... -> %PLACE_NAME".
- If the path cannot be found, print "No such optimal path to %DEST"
- Possible cause: The state of the destination is close.
The output of LIMITED_PATH:
- If the path can be found, print the optimal path from the current origin to the destination, in the format "Limited %CONSIDERATION : %PLACE_NAME -> %PLACE_NAME -> ... -> %PLACE_NAME"
- If the path cannot be found, print "No such limited path %DEST"
- Possible cause 1: The state of the destination is close.
- Possible cause 2: The destination cannot be accessed within %MAX stops.
The output of END_OF_INSTRUCTION:
Print "End of instructions".
A new line is required at the end of each instruction output.