Description
In computer science, Base64 is a binary-to-text encoding method. Here is how Base64 encoding works.
Given a string that contains ASCII characters:
- First, you need to turn each character to its ASCII number then to its 8-bits binary number,
- Second, connect all the binary numbers, from the first binary, and replace every 6 bits by its corresponding Base64 character, where such mapping is provided in the Base64 index table below.
- Last, if the total length of all the binary numbers (in terms of bits) is not a multiple of 6, add zero until the total length is a multiple of 6, and for every 2 zero you add, add a '=' character to your encoded string.
ouo.
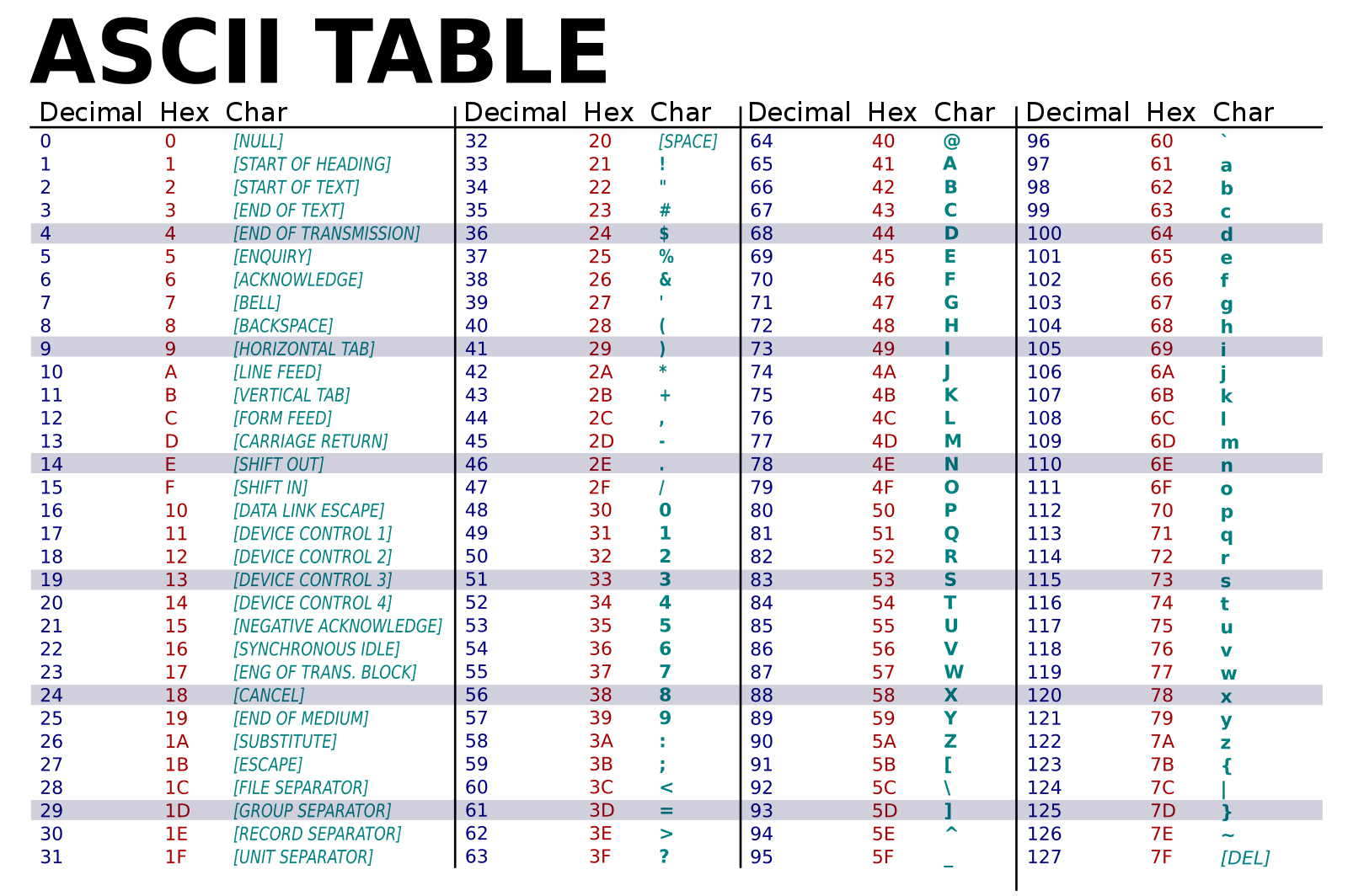
The ASCII code table is as follows:
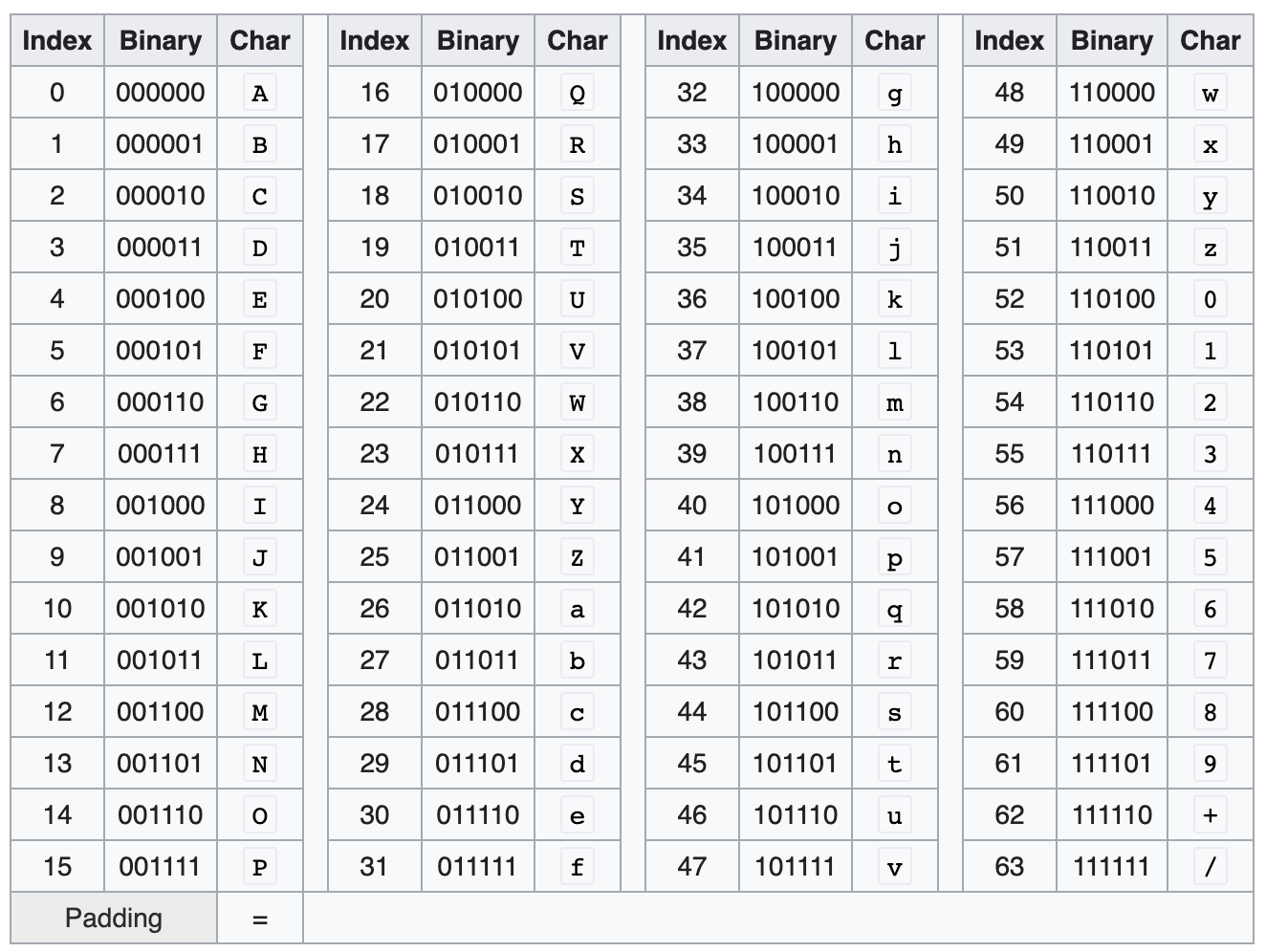
The Base64 index table is as follows: (From WIKI)
Sample Input 1:
Turn the string "Man" to ASCII numbers:
M = 77, a = 97, n = 110.
Turn ASCII numbers to 8-bits binary numbers:
77 = 01001101, 97 = 01100001, 110 = 01101110,
010011 / 010110 / 000101 / 101110
Replace every 6 bits by the corresponding character as the table above:
010011 = T / 010110 = W / 000101 = F / 101110 = u
Base64 encoding of "Man" is "TWFu"
Sample Input 2:
Turn the string "Ma" to ASCII numbers:
M = 77, a = 97.
Turn ASCII numbers to 8-bits binary numbers:
77 = 01001101, 97 = 01100001.
010011 / 010110 / 0001
The length is not a multiple of 6, add zero until it becomes a multiple of 6. So we add 2 zero:
010011 / 010110 / 000100
Replace every 6 bits by the corresponding character as the table above:
010011 = T / 010110 = W / 000100 = E
For every 2 zero you add, add 1 '=' to the Base64 encoding result. So we add 1 '=':
Base64 encoding of "Ma" is "TWE="
Sample Input 3:
Turn the string "M" to ASCII numbers:
M = 77.
Turn ASCII numbers to 8-bits binary numbers:
77 = 01001101.
010011 / 01
The length is not a multiple of 6, add zero until it becomes a multiple of 6. So we add 4 zero:
010011 / 010000
Replace every 6 bits by the corresponding character as the table above:
010011 = T / 010000 = Q
For every 2 zero you add, add 1 '=' to the Base64 encoding result. So we add 2 '=':
Base64 encoding of "M" is "TQ=="
The class inheritance hierarchy of this problem is given below:
class Codec { protected: bool encoded; string code_str; public: Codec(string& code_str): code_str(code_str), encoded(false) {} virtual void encode() = 0; virtual void decode() = 0; virtual void print(ostream& os) const = 0; virtual bool is_encoded() const = 0; }; class Base64Codec: public Codec { private: // Given 6-bits binary number, return with the Base64 encode character char encodeCharacter(int binaryNumber) const; public: // Inherit from base class Base64Codec(string& code_str): Codec(code_str) {} // TODO: Encode the code_str void encode() override; // Decode the code_str void decode() override; // Print the code_str void print(ostream& os) const override; // Get code_str status bool is_encoded() const override; };
In this problem, you only need to implement the member function encode() of class Base64Codec.
Note:
1. We have implemented the encodeCharacter(int binaryNumber) function in class Base64Codec for you, whose details are further explained below:
Given a binaryNumber in decimal, representing a 6-bits binary number, encodeCharacter() returns the corresponding character to Base64 encoding.
Example:
binaryNumber = 19(decimal) = 010011(binary),
encodeCharacter(binaryNumber) returns character 'T'
2. You should choose 'C++11' on submission.
Input
The input contains 1 line: a string S.
The string will only contain characters A~Z, a~z, 0~9, space, comma(',') and period('.')
It is guaranteed that:
1 <= |S| <= 2000
Output
The output contains only 1 line: the Base64 encoding of the given string.
With a new line character after your output.