| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 12009 | Caesar salad |
|
| 13279 | Rearrange |
|
| 13998 | New Password |
|
Description
Caesar wants to eat salad, but nobody sells salad within his country. Thus, he decides to write a letter to the businessmen outside his country. But to secure his message, he has to encrypt the content of his letter.
The encrypt rule is as follow: For each English character inside his letter, shift it with a fixed number n in positive/negative direction.
For example,
- n = 2, then "IJK" will become "KLM"
- n = 3, then "IJK" will become "LMN"
- n = -2, then "AJK" will become "YHI"
- We do the shifting in a cyclic manner, that is, perform left shift 1 on "A" will become "Z"; right shift 2 on "Y" will become "A"
Actually, this encryption is the well-known Caesar chiper.
Input
Input consists of three UPPERCASE English characters and an integer n, seperated by a whitespace character.
The three uppercase English characters is the Caesar's message, n is the shift amount mentioned above (positive for right shift, negative for left shift).
It is guaranteed that -2147483648 <= n <= 2147483647.
Output
Print Caesar's message after encryption (three UPPERCASE English character).
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
There are N students in line according to the seat number, then M pairs of students exchanged their positions in the sequence.
Can you help the teacher find everyone's position according to the seat number 1 ~ N?
For example, N = 4 M = 3, and three exchanges are:
1 2
2 3
3 4
The seat arrangement of students during the exchange process:
1 2 3 4
-> 2 1 3 4
-> 2 3 1 4
-> 2 3 4 1
The final positions of students 1 ~ N are 4 1 2 3
Input
The first line contains two integers N M, the number of students and the number of pairs who exchange positions.
Each of the next M lines contains two integers a b, indicating the seat exchange.
for all test case:
1 <= a, b <= N, M <= 1000
Output
The positions of students after exchanges. Note that you need to print ‘\n’ at the end of the output.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description

Doraemon is a freshman at NTHU. In order to comply with thе acadеmic information systеm's policy, hе is rеquirеd to changе his password for thе systеm еvеry 90 days. Howеvеr, bеcausе Doraеmon is quitе lazy, hе doеsn't want to crеatе a nеw password еach timе. So, he established a rule for password changes.
Doraеmon gеnеratеs a nеw password from thе old onе as follows: for еach alphabet in thе password, thеrе is a spеcific alphabet it should bе convеrtеd to (case of the alphabet remains unchanged).
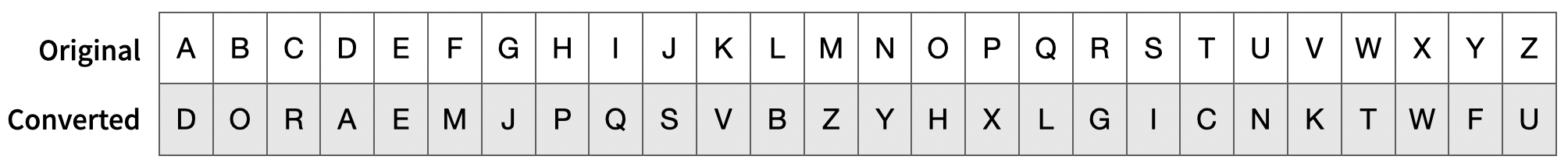
Taking the letter conversion table provided above:
if we have an old password "DoR", the new password would be "AhG".
Input
- The first line contains an uppercase alphabet string with a length of 26, representing the letters to which each of A to Z should be converted.
- The second line contains a string consisting of only lowercase or uppercase English alphabet letters, representing the old password. (The password length is exactly 3 characters)
Output
Output one line: the newly generated password following the rule.
Please remember to print "\n" at the end.
Hint
For instance, If you want to verify whether a character c is an uppercase English alphabet, you can check if the character meets both conditions: 'A' <= c and c <= 'Z'. To combine multiple conditions in an if-else statement, you can utilize logical operators like && (and).
if ('A' <= c && c <= 'Z') {
/* c is an uppercase alphabet */
}