| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 11014 | Encoding and decoding |
|
| 11422 | Shape |
|
| 11443 | 3DShape |
|
| 12715 | BigInt++ |
|
| 13131 | Max-Heap Using Polymorphism |
|
| 13182 | Twenty One |
|
| 13203 | Twenty One - Guard, Banker, and Players |
|
Description
The task is to define the class ‘RleCodec’ for run-length encoding.
About implementing the virtual function:
We have the base class ‘Codec’ as an interface. The member functions in ‘Codec’ are pure virtual functions. Therefore we need to implement those virtual functions in the derived class ‘RleCodec’. The functions ‘decode’, ‘show’, ‘is_encoded’ are already done. The only function you need to complete is ‘RleCodec::encode’ in ‘function.cpp’.
In ‘main.cpp’, we see two functions having an argument of type ‘Codec&’:
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, Codec& data);
void encode_decode(Codec& data);
Since ‘RleCodec’ is a derived class of ‘Codec’, we may pass an object of ‘RleCodec’ to the above two functions by reference as if it is an object of ‘Codec’. Calling ‘data.show(os);’ will invoke the virtual function of the corresponding derived class.
About run-length encoding:
The rule of run-length encoding is simple: Count the number of consecutive repeated characters in a string, and replace the repeated characters by the count and a single instance of the character. For example, if the input string is ‘AAADDDDDDDBBGGGGGCEEEE’, its run-length encoding will be ‘3A7DBB5GC4E’, because there are three A’s, seven D’s, … etc. Note that we do not need to encode runs of length one or two, since ‘2B’ and ‘1C’ are not shorter than ‘BB’ and ‘C’.
In ‘function.h’, we add the class ‘DummyCodec’ as a sample of implementing a derived class of the base class ‘Codec’. You do not need to change anything in ‘function.h’. The only function you need to write for this problem is the function ‘RleCodec::encode’ in ‘function.cpp’.
Hint: std::stringstream could be useful in solving this problem. Please refer to ‘RleCodec::decode’ for how to use std::stringstream.
You only need to submit ‘function.cpp’. OJ will compile it with ‘main.cpp’ and ‘function.h’.
We have already provided partial function.cpp belowed.
Note that if you can't use "auto".
For codeblock, go to the codeblock menu Settings --> Compiler ... --> Compiler flags and check Have g++ follow the C++11 ISO C++ language standard [-std=c++11]
For command line compiler, use g++ myprog.cpp -std=c++11 -o myprog
main.cpp
function.h
function.cpp
Input
A line contains of several characters .
Output
There are four lines.
The first and second lines are dummy encoding and decoding. You don't need to implement it.
The third and forth lines are RLE encoding and decoding.
Each line is followed by a new line character.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11014.cppPartial Judge Header
11014.hTags
Discuss
Description
Warning: You are not allowed to use malloc and free
Following the lecture slide :
Giving a bass-class Shape and 3 derived class : Triangle, Rectangle, Circle
You need to calculate the area and the perimeter of each shape.
note : You need to do some basic check: if the given information cannot form a shape (e.g. height of the rectangle is negative number....etc), then the area and perimeter would be both 0)
Input
There are only 3 shapes in this problem :
- Triangle, following by its 3 edges. (e.g. Triangle 3 4 5)
- Rectangle, following by its width and height. (e.g. Rectangle 5 7)
- Circle, following by its radius and the value of pi. (e.g. Circle 2 3.14)
Output
Ouput the total area and perimeter of all the shapes.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11422.cppPartial Judge Header
11422.hTags
Discuss
Description
Warning: You are not allowed to use malloc and free
Giving a bass-class Shape3D and 4 derived class : Sphere (球體), Cone (圓錐), Cuboid (長方體), Cube (立方體)
You need to calculate the volume of each shape.
PS:
V of Sphere: V = 4/3 π r3
V of Cone: V = 1/3 π r2 h

note : Remember to do some basic check, if the input is illegal (e.g. length < 0, pi < 0 .....) then the volume should be 0.
You don't need to consider the scenario like Cuboid -1 -2 3, volume would be 0 instead of 6.
Hint1: Be careful the type of volume is double. 4/3=1 (int), so it should be 4.0/3.0
Hint2: You only need to implement the constructors.
Hint3: Note that Cube inherited Cuboid not Shape3D.
Input
There are only 4 shapes in this problem :
- Sphere, following by its radius and pi. (e.g. Sphere 30 3.14)
- Cone, following by its radius of bottom plane, height and pi. (e.g. Cone 3 100 3.14)
- Cuboid, following by its length, width and height. (e.g. Cuboid 2 3 7)
- Cube, following by its length. (e.g. Cube 2)
Output
Ouput the total volume of all the shapes.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11443.cppPartial Judge Header
11443.hTags
Discuss
Description
"int" is too small to store large numbers!
That's why you decided to implement your own data type, BigInt.
You need to implement 7 basic functions:
1. Constructor. It is initalized by a string representing a non-negative integer without leading zeroes (despite "0" itself).
2. Destructor.
3,4,5,6. ++x, x++, --x, x--, as in the C/C++ standard.
7: char* to_s(): returns a duplicate of the number in char*, e.g., "123".
UPDATE:
Note that you don't need to implement negative numbers. When the number is 0 and you have to decrement it, you can ignore the operation.
Input
The first line contains an integer T, representing the number of testcases that follow.
For each testcase, a non-negative integer less than pow(10, 1023) is given in the first line.
An integer Q follows, representing the number of operations regarding the testcase.
Q lines follow, each in the form of "B++", "++B", "B--", or "--B", the effect of which is the same as specified in the C/C++ standard.
Output
For each operation, print the result in one line, without leading zeroes.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12715.cppPartial Judge Header
12715.hTags
Discuss
Description
A. Definition of Max-Heap
A heap is a complete binary tree.
A max-heap is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater
than or equal to the values in the children of that node.
B. Implementation of the Max-Heap Data Structure
1. Array:
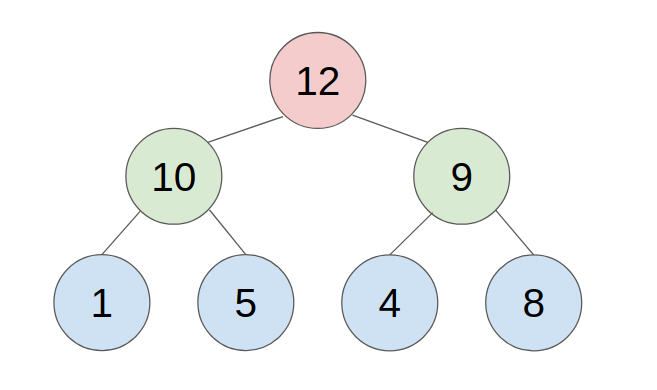
An approach to store a max-heap is to use a single, contiguous block of memory cells, i.e., an array, for the entire tree. We store the tree’s root node in the first cell of the array. (Note that, for ease of implementation, we ignore the 0th cell and start from the 1st cell.) Then we store the left child of the root in the second cell, store the right child of the root in the third cell, and in general, continue to store the left and right children of the node found in cell n in the cells 2n and 2n+1 respectively. With this technique, the tree shown below
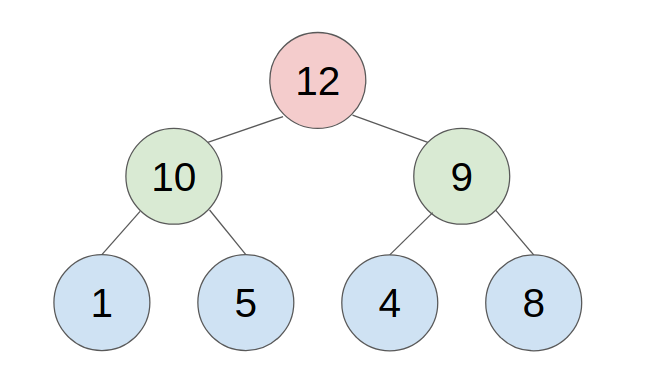
would be stored as follows
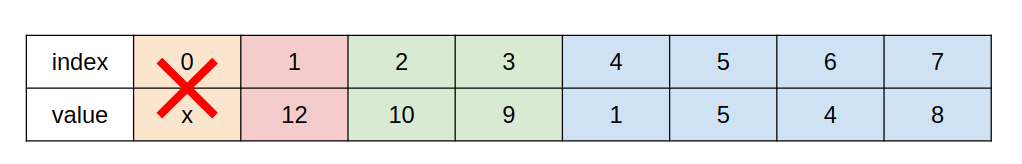
2. Linked list:
We set a special memory location, call a root pointer, where we store the address of the root node. Then each node in the tree must be set to point to the parent and left or right child of the pertinent node or assigned the NULL value if there are no more nodes in that direction of the tree.
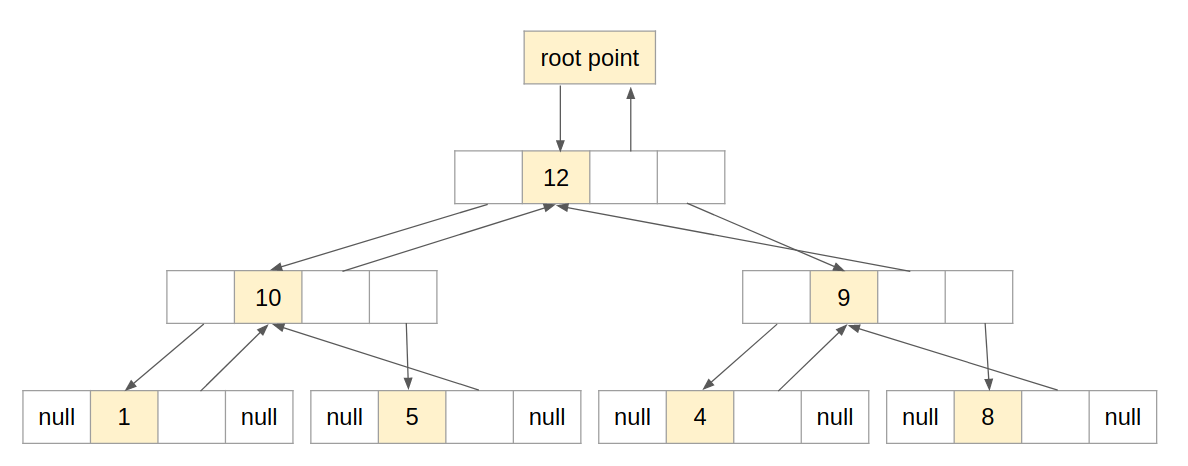
C. Method to push/pop an element
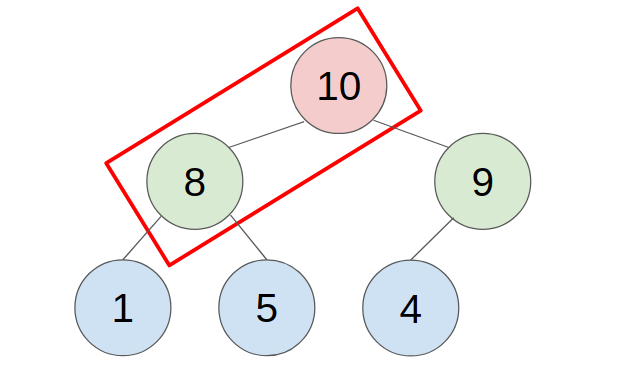
1. PUSH
- put the new element in the last place of the heap.
- compare with the parent, swap them until the parent is greater or equal to the new element.
- example: push 11 to this heap
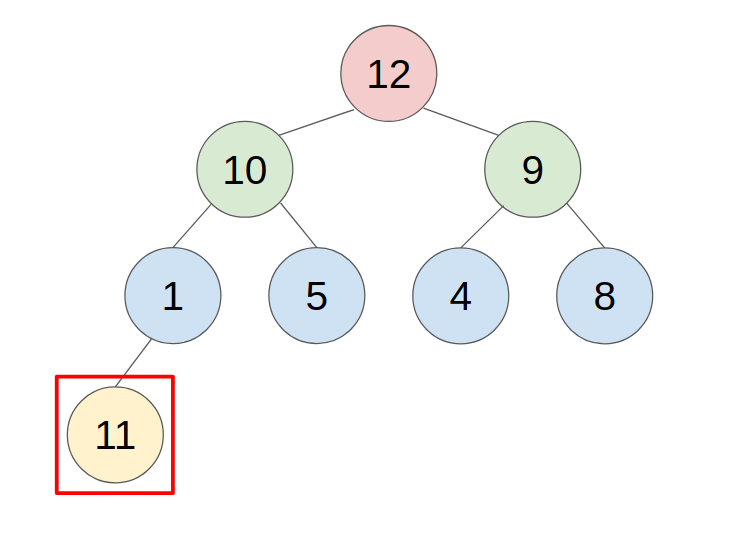
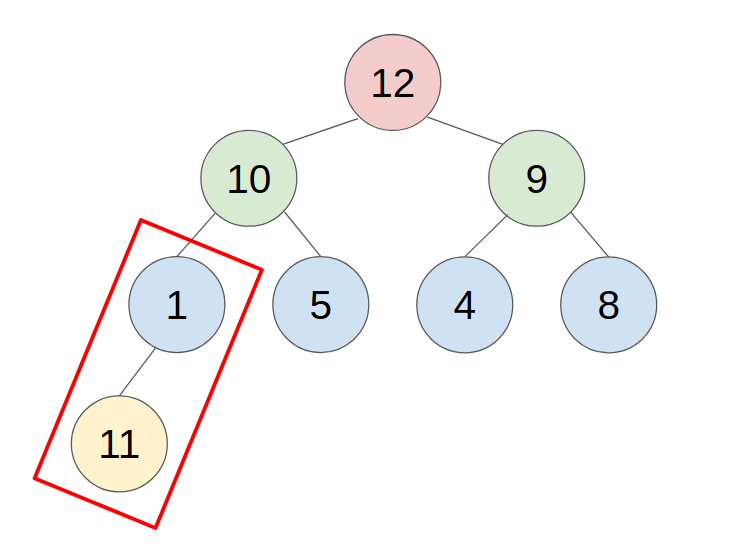
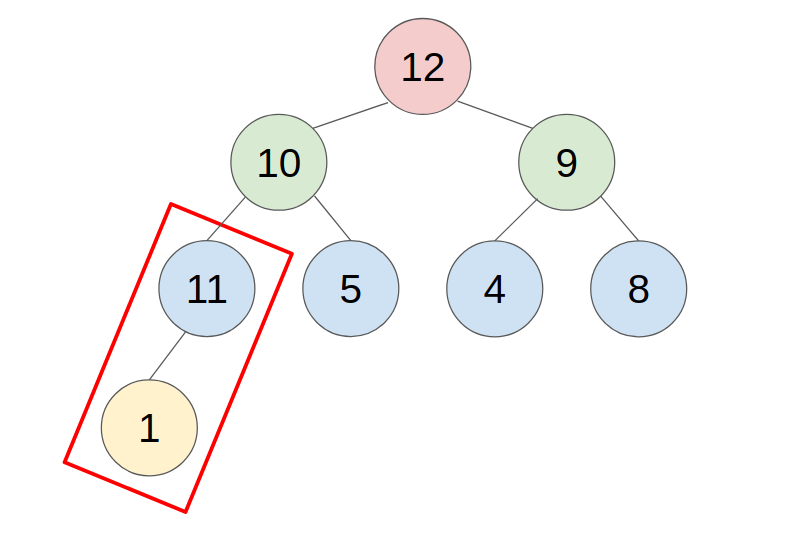
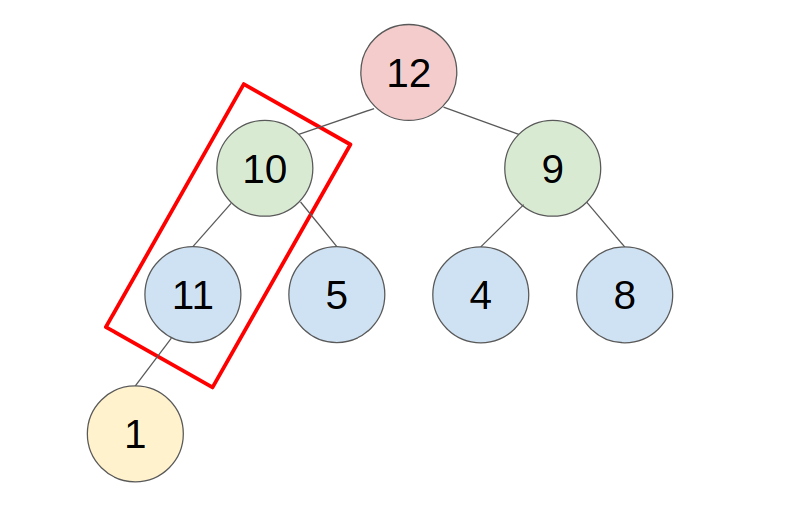
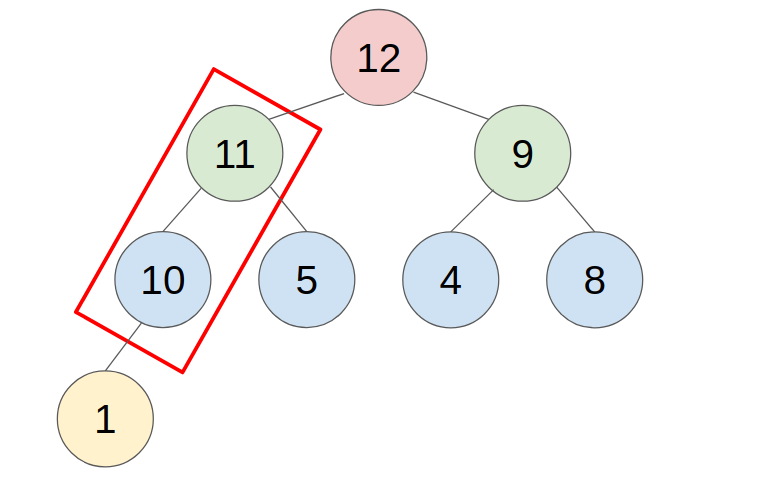
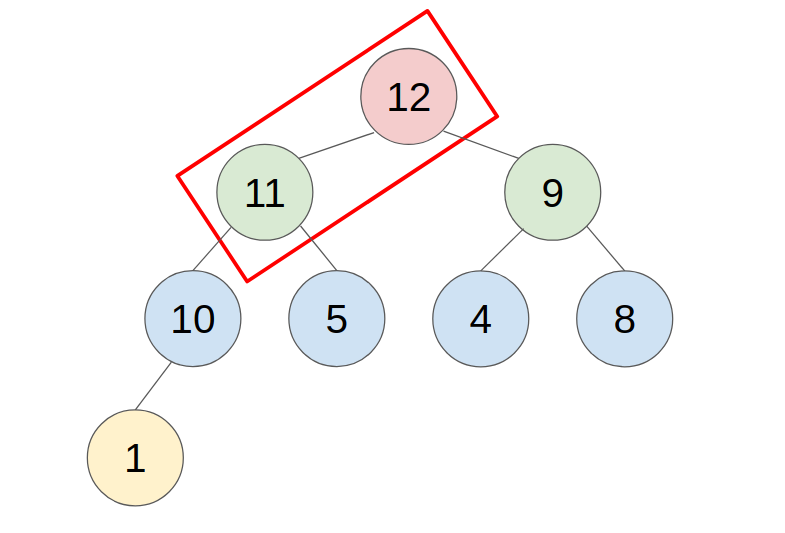
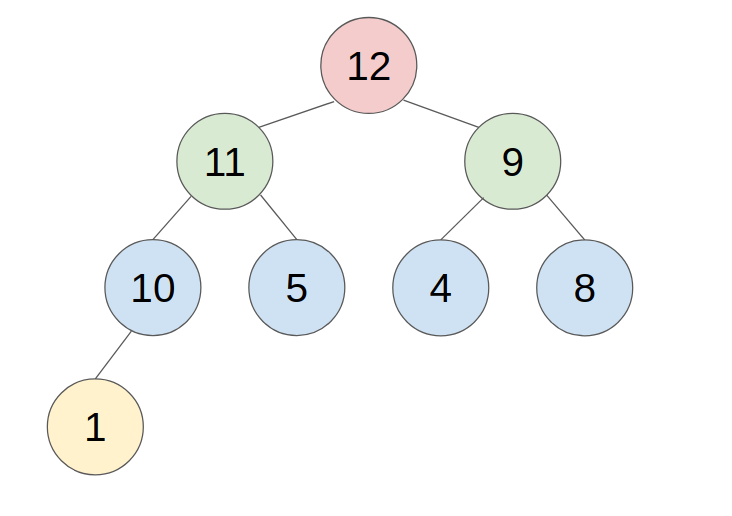
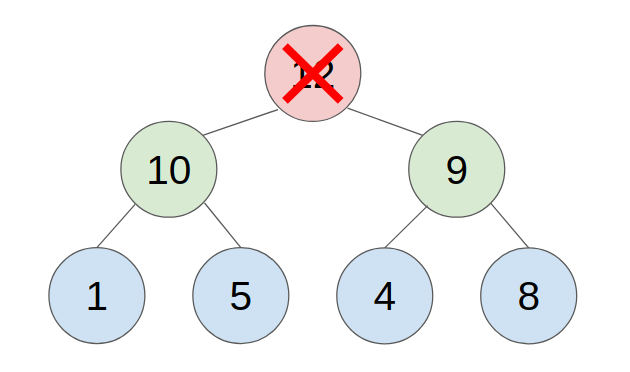
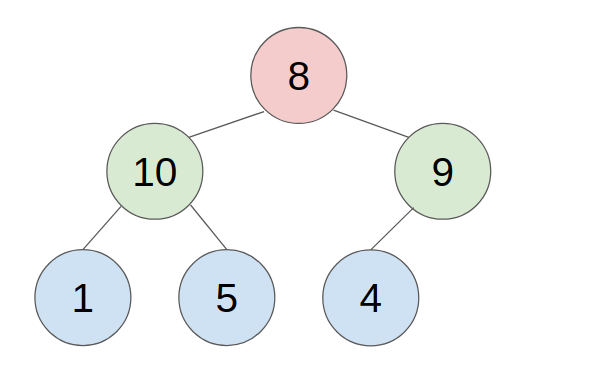
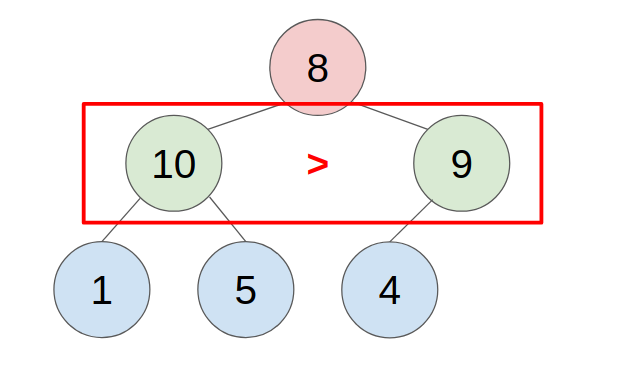
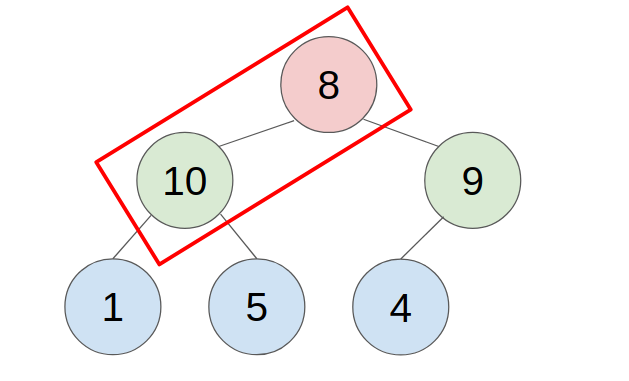
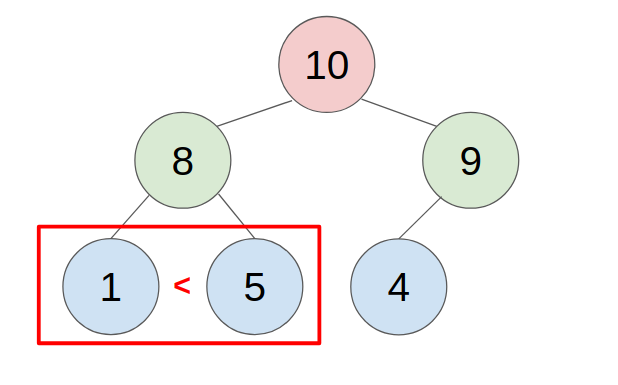
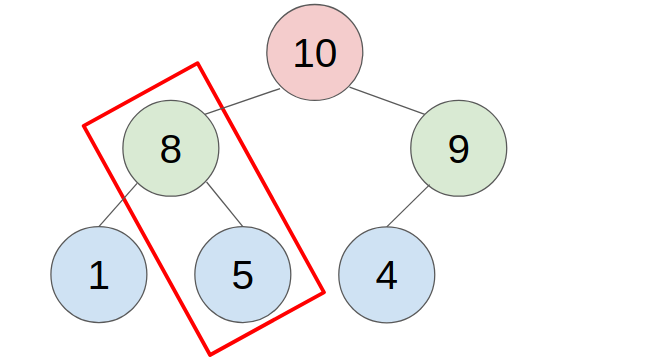
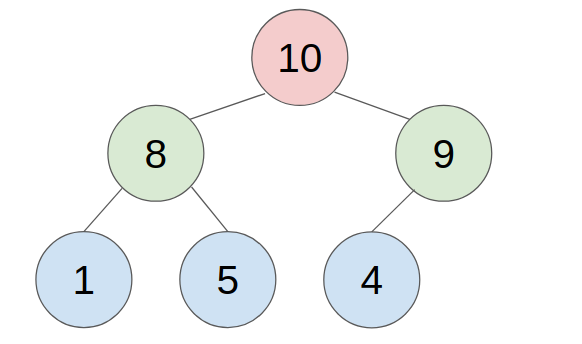
2. POP
- put the last element to the top(root) of the heap.
- compare with the greater child, swap them until all child is smaller than it.
- example:
REQUIREMENTS:
Implement the constructor, push(), max(), pop() member functions of both the Array_MAX_HEAP and List_MAX_HEAP classes and deleteTree() of List_MAX_HEAP class.
Hint
For easy to solve this problem, you can call findparent(int cnt, ListNode *root) to return a ListNode which is the parent of node[cnt] in List_MAX_HEAP class.
Input
The first line contains an integer n.
Each of the next n lines has an instruction.
The instruction will be either:
- A_push: push a new element ai into the array_max_heap.
- L_push: push a new element ai into the list_max_heap.
- max: show the max element. if the max-heap is empty, print -1.
- A_pop: show and pop the max element in the array_max_heap. if the max-heap is empty, print -1.
- L_pop: show and pop the max element in the list_max_heap. if the max-heap is empty, print -1.
- size: show the size of the heap.
For all testcase:
1 <= n <= 1000, 0 <= ai < 231
(2/6) only A_push, L_push or size instruction
(2/6) only A_push, L_push, size or max instruction
(2/6) contains all instruction
Output
For max, A_pop or L_pop instruction, print the max element in the heap.
For size instruction, print the size of the heap.
Remember to print \n at the end of output.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
13131.cppPartial Judge Header
13131.hTags
Discuss
Description
Notice: Please use C++11 or above to submit this problem!

After watching the movie 21, Kuo is curious about casino.
There is a casino which opens N days in this month.
There will be two kind of events in a day.
- Guest <Someone> <Money> <Skill>. It means <Someone> enter the casino with <Money> money. <Someone> are their names, <Money> is the amount of money with them, and <Skill> is how well they play. If <Someone> are already in the casino or are blacklisted, ignore this event.
- Win <Someone> <Money>. It means <Someone> win <Money> money in a play from the casino. <Money> may be positive or negative. If <Someone> are not in the casino or are blacklisted, ignore this event.
Whenever someone enter the casino, they have to pay T entrance fee to the casino. The enterance fee may change every day.
Whenever one become bankrupt, they will be kicked out of the casino and be blacklisted.
If the amout of money someone win in a play exceed (that is, >) twice of their <Skill>, they will be seen as cheaters, kicked out of the casino, and blacklisted. (The casino still has to pay the money they win to them.)
Someone blacklisted are not permitted to enter the casino. In particular, when someone blacklisted wants to enter the casino, they won't be charged the enterance fee.
Note: If someone have to pay X money but they only have Y money where Y <= X, they will only pay Y money and become bankrupt.
At the end of each day, everyone will leave the casino.
Please help Kuo-chan find how much income the casino gets in this month and who are blacklisted.
Input
The first line of the input contains a number N — the number of days in this month.
The following contains N blocks.
The first line of each block is Casino Q T — it means there will be Q events and the entrance fee is T this day.
The next Q lines is one of the following:
- Guest <Someone> <Money> <Skill>
- Win <Someone> <Money>
N <= 1000, Q <= 100.
There will be at most 1000 different people come to the casino; that is, there are at most 1000 people with different names. Therefore, there will be at most 1000 people blacklisted.
All number is within the range of int.
Output
You should print a number U in the first line — how much income the casino gets in this month.
If there are K people blacklisted in this month, you should output their names in K lines in the order they get blacklisted.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
13182.cppPartial Judge Header
13182.hTags
Discuss
Description
After watching the movie 21, JN is curious about casino.
There are one banker and one guard in the casino. They have banker_ski and guard_ski skill respectively.
There are N players playing twenty one. The i-th of them has mi dollars and skii skill.
There will be K rounds of twenty one in total today.
In each round, each of the players place their bets beti first, then draw some cards.
The banker draws the cards last.
Let A be the sum of the i-th player's cards, B be the sum of the banker's.
Then:
- A > 21 and B > 21, nothing happens.
- A <= 21 and (B > 21 or A > B), the i-th player wins.
- B <= 21 and (A > 21 or B >= A), the i-th player loses.
For the banker:
- If the i-th player wins, the banker has to pay beti dollars to the i-th player.
- If the i-th player wins and skii < banker_ski, the banker has to pay the i-th player 10 * (the sum of the i-th player's cards) as a bonus.
- Furthermore, if the i-th player wins and the sum of the i-th player's cards is equal to 21, the banker has to pay 2*(bets + bonus) to the i-th player. (bonus may be equal to 0)
- For example, if the sum of the i-th player's cards is 21, skii < banker_ski, and beti = 1000, then the banker has to pay (1000+10*21)*2 to the i-th player.
- Whenever a player becomes bankrupt, the banker calls the guard to kick the player out and gives the guard 100 dollars.
- Whenever a player is seen to be a cheater; that is, 2*skii < the amount of money that the banker has to pay to the player, the banker calls the guard to kick the player out and gives the guard 100 dollars.
For the guard:
- When the guard has to kick i-th player who is a cheater out, if guard_ski < skii, the guard has to pay (skii - guard_ski) dollars to the i-th player; if guard_ski >= skii, the guard doesn't have to pay.
- When the guard has to kick a bankrupt player out, the guard doesn't have to pay.
For the player:
- If the i-th player loses, the i-th player has to pay beti dollars to the banker.
- If the i-th player loses but beti >= the amount of money the i-th player has now, the i-th player only has to pay all the money they have. In this case, the i-th player becomes bankrupt.
- If the i-th player is already kicked out of the casino, ignore any of the i-th player's bets and cards.
The banker and the guard have 0 dollars at first.
Input
The first line of the input contains two numbers — guard_ski and banker_ski.
The second line of the input contains a number N — the number of players.
Each of the next N lines contains a string namei and two numbers mi and skii — the name, money, and the skill the i-th player has.
The next line contains a number K — there will be K rounds of twenty two today.
The following contains K blocks, i = 1, ..., N.
There will be a string namei and a number beti in the 2i - 1 line — the i-th player's name and the bets they place.
There will be some numbers c1, ..., ct in the 2i line — the cards the i-th player has.
The last line of each block will be some numbers c1, ..., ct — the cards the banker has.
N, K <= 500.
All the other numbers <= 5*104.
Output
You should print N+1 lines in total.
The first line of output should contains two numbers guard_money and banker_money — the money the guard and the banker gets.
Each of next N lines should contains a string namei and moneyi — the name of the i-th player and the money they have after playing.