| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 13075 | Clock |
|
| 13076 | Dietary Guideline |
|
Description
Complete an existed class Clock. There is also had a function named sec2clk(), understand it and use it, it may help.
Clock sec2clk(int s) – Turn s seconds into a clock, and return it. For example:
- s = 3661 => 01:01:01
- s = 86401 => 00:00:01
- s = -1 => 23:59:59
Clock
Private Variables:
- h(unsigned int) represents to hour.
- m(unsigned int) represents to minute.
- s(unsigned int) represents to second.
Constructors:
- Clock(unsigned int _h, unsigned int _m, unsigned int _s) – Should initalize h to _h%24, m to _m%60 and s to _s%60.
Public Methods:
- Clock operator+(const Clock &other) – Should return a Clock which is the addition of the two clocks.
- Clock operator-(const Clock &other) – Should return a Clock which is the subtraction of the two clocks.
Need consider time carry(時間進位) and time overflow(時間溢位). For example:
- 00:59:59 + 00:00:01 = 01:00:00
- 23:59:59 + 00:00:01 = 00:00:00
- 00:00:00 - 00:00:01 = 23:59:59
note that you may use Clock::clk2sec() and sec2clk().
- bool operator>(const Clock &other) – Should return true if the time of clock is bigger than others; otherwise return false.
Need consider time carry(時間進位) and time overflow(時間溢位). For example:
- 01:00:00 > 00:59:59 is true
- 00:00:01 > 23:59:59 + 00:00:01 is true
note that you may use Clock::clk2sec().
- bool operator<(const Clock &other) – Should return true if the time of clock is smaller than others; otherwise return false.
- bool operator>(const unsigned int ui) – Should return true if the total seconds of clock is bigger than ui%86400; otherwise return false.
- bool operator<(const unsigned int ui) – Should return true if the total seconds of clock is smaller than ui%86400; otherwise return false.
- bool operator==(const Clock &other)– Should return true if the time of clock is equal to others; otherwise return false.
- bool operator==(const unsigned int ui) – Should return true if the total seconds of clock is equal to ui%86400; otherwise return false.
- unsigned int clk2sec() const – Calculate the total seconds of clock and return (no need implement).
- friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Clock &clk) – For print out a Clock variable directly (no need implement).
Input
No need to handle input. (Input would be number 1~5 to represent the index of test-case)
Output
Depend on test case show in main.cpp.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
13075.cppPartial Judge Header
13075.hTags
Discuss
Description
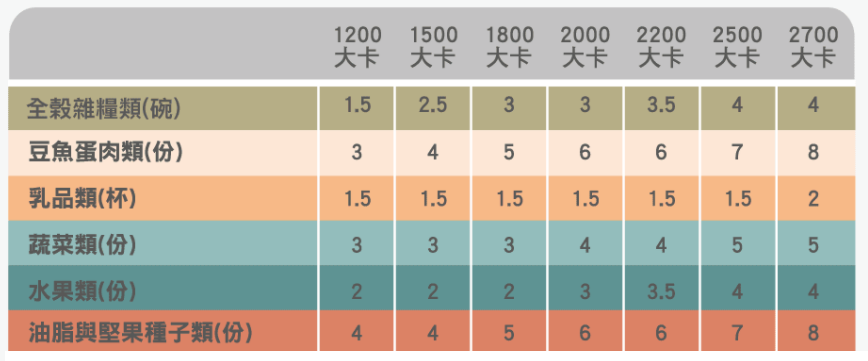
Base on the dietary guideline from Ministry of Health and Welfare(衛福部) in Taiwan. We can divide food we eat into six categories: grains(全穀雜糧類), protein(蛋豆魚肉類), dairy(乳品類), vegetables(蔬菜類), fruits(水果類), fats and nuts(油脂與堅果種子類).
According to the figure below, we can know how many servings of each of these six foods should be consumed based on how many calories are consumed in a day.
To simplify, we only consider calories less than or equal to 1500 (considered as 1500 in the figure above), 1500 to 2000 (as 2000) and greater than 2000 (as 2500).
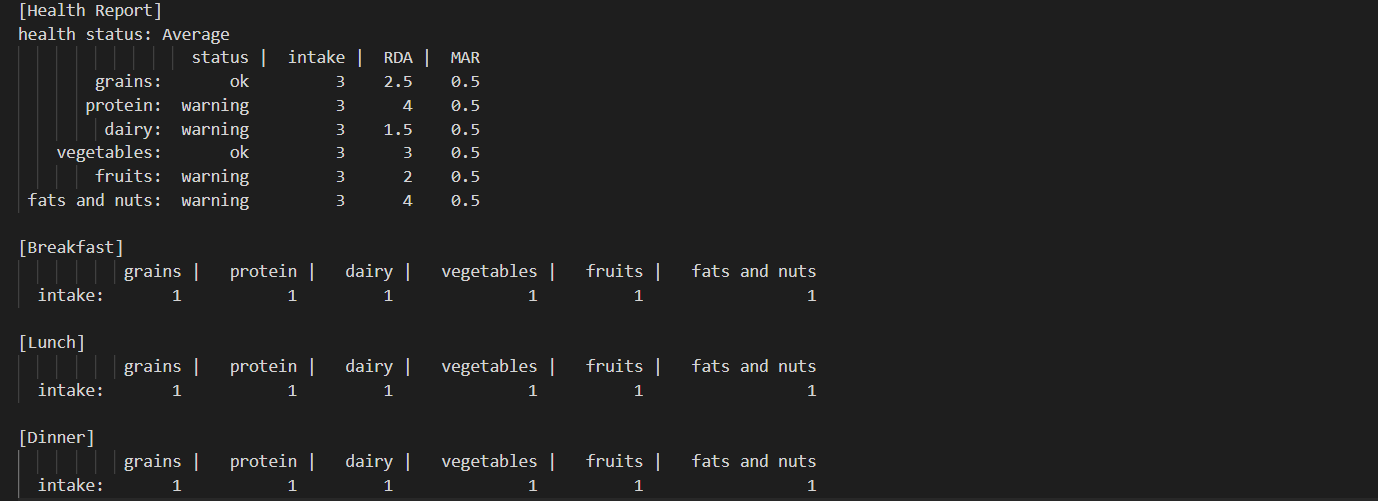
Your final goal is to print out a health report, based on what this person had for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. A health report based on a human who need to consume less than or equal to 1500 may look like this:
First,
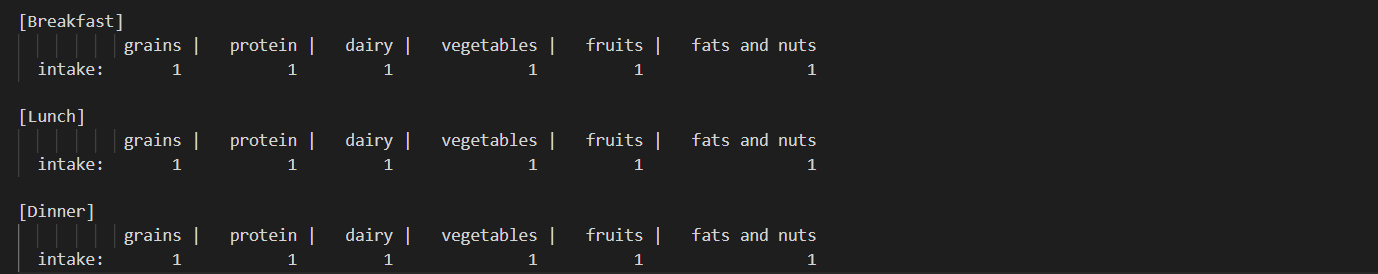
- the figure above shows how many servings of each of six kinds of food are included in this person’s breakfast (also lunch and dinner).
Second,

- RDA is the short of Recommended Dietary Allowance based on the dietary guideline.
- intake is the total servings of each of six kinds of food in the person’s daily meals (breakfast + lunch + dinner).
- MAR is the short of Maximum Allowable Range, to simplify we always set to 0.5.
- The status of one kind of food is based on the intake and RDA of this food. If the intake is in the range of RDA +/- MAR, the status should be “ok”; otherwise, should be “warning”.
Finally,

- The health status is based on the total number of risks (how many “warning” you get). If total number of risks is less than or equal to 2, the status should be “Excellent”; if it is 3 or 4, the status should be “Average”; if it is larger or equal to 5, the status should be “Poor”.
/*******************************************************************\
You don’t need to handle the output format, and only need to implement seven functions below and correct the access method for classes Breakfast, Lunch, Dinner to be derived from class DietaryGuideline.
Thus, [Please read and understand the main.cpp first before you started to code]. Now let’s take a look of the functions you need to implement.
void DietaryGuideline::risksAnalysis(string *g_status, string *p_status, string *d_status, string *v_status, string *fr_status, string *fa_status, string *h_status) – Should change all the food_status with the rules mentioned above based on variable food (grains, protein, dairy…) and rda_food (rda_grains, rda_protein, rda_dairy…).
note: *g_status is for the string pointer of grains_status, *p_status is for pointer of protein_status (so as to *d_status, *v_status, *fr_status and *fa_status). *h_status is for the string pointer of health_status.
void Breakfast::eat(double g, double p, double d, double v, double fr, double fa) – should update the food variable in Breakfast and DietaryGuideline.
note: g represents how many servings of grains were consumed, p represents as protein, d represents as dairy, v represents as vegetables, fr represents as fruits, fa represents as fats and nuts.
void Lunch::eat(double g, double p, double d, double v, double fr, double fa) – Similar to Breakfast::eat().
void Dinner::eat(double g, double p, double d, double v, double fr, double fa) – Similar to Breakfast::eat().
void Human::eatBreakfast(double g, double p, double d, double v, double fr, double fa) – Should call Breakfast::eat().
note: g, p ,d, c, fr, fa represents how many servings of each kinds of food were consumed, respectively.
void Human::eatLunch(double g, double p, double d, double v, double fr, double fa) – Should call Lunch::eat().
void Human::eatDinner(double g, double p, double d, double v, double fr, double fa) – Should call Dinner::eat().
main.cpp
Input
No need to handle input. (Input would be number 1~5 to represent the index of test-case)
Output
Depend on test case show in main.cpp.